

 intraoprative data:
intraoprative data:With displaced posterior table fractures, the risk of dural injury is unacceptably high.
In this case of frantal fracture , exploration for dural and repair was done.
In this case of frantal fracture , exploration for dural and repair was done.



To prevent late complications, these sinuse generally obliterated. The oblitrating material are muscle and fat from the thight.

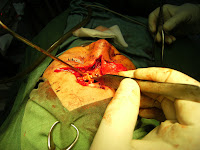

With severe comminution of the posterior table, cranialization is the option.
A muscular flap can be used to separate the nasal and frontal cavities in patient as the cribriform plate was injured and thus augment the skull base and dural repair.
The anterior table can be reposioned and fixed by miniplate and scrow.
The anterior table can be reposioned and fixed by miniplate and scrow.
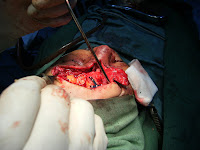




postoperative finding:


Treatment Options for fractures of the posterior table
Ø Nondisplaced without CSF leak
Observation
Ø Nondisplaced with CSF leak
Conservative management of CSF leak with progression to sinus exploration if no resolution in 4–7 days
Ø Displaced (>one table width)
Sinus exploration, repair of dura, obliteration or cranialization depending on involvement of the posterior table.
Ø Involvement of the nasofrontal outflow tract
Obliteration or~and cranialization